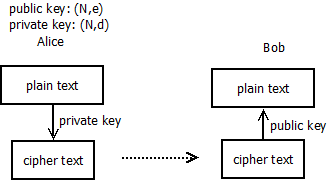
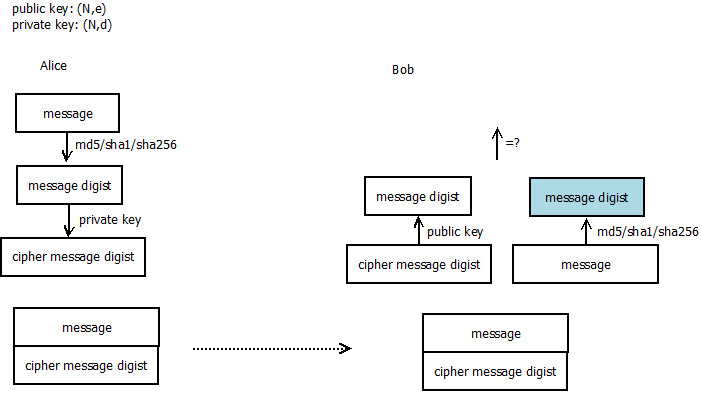
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Certificate generation module.
"""
from OpenSSL import crypto
TYPE_RSA = crypto.TYPE_RSA
TYPE_DSA = crypto.TYPE_DSA
def createKeyPair(type, bits):
"""
Create a public/private key pair.
Arguments: type - Key type, must be one of TYPE_RSA and TYPE_DSA
bits - Number of bits to use in the key
Returns: The public/private key pair in a PKey object
"""
pkey = crypto.PKey()
pkey.generate_key(type, bits)
return pkey
def createCertRequest(pkey, digest="md5", **name):
"""
Create a certificate request.
Arguments: pkey - The key to associate with the request
digest - Digestion method to use for signing, default is md5
**name - The name of the subject of the request, possible
arguments are:
C - Country name
ST - State or province name
L - Locality name
O - Organization name
OU - Organizational unit name
CN - Common name
emailAddress - E-mail address
Returns: The certificate request in an X509Req object
"""
req = crypto.X509Req()
subj = req.get_subject()
for (key,value) in name.items():
setattr(subj, key, value)
req.set_pubkey(pkey)
req.sign(pkey, digest)
return req
def createCertificate(req, (issuerCert, issuerKey), serial, (notBefore, notAfter), digest="md5"):
"""
Generate a certificate given a certificate request.
Arguments: req - Certificate reqeust to use
issuerCert - The certificate of the issuer
issuerKey - The private key of the issuer
serial - Serial number for the certificate
notBefore - Timestamp (relative to now) when the certificate
starts being valid
notAfter - Timestamp (relative to now) when the certificate
stops being valid
digest - Digest method to use for signing, default is md5
Returns: The signed certificate in an X509 object
"""
cert = crypto.X509()
cert.set_serial_number(serial)
cert.gmtime_adj_notBefore(notBefore)
cert.gmtime_adj_notAfter(notAfter)
cert.set_issuer(issuerCert.get_subject())
cert.set_subject(req.get_subject())
cert.set_pubkey(req.get_pubkey())
cert.sign(issuerKey, digest)
return cert
cakey = createKeyPair(TYPE_RSA, 1024)
careq = createCertRequest(cakey, CN='Certificate Authority')
cacert = createCertificate(careq, (careq, cakey), 0, (0, 60*60*24*365*5)) # five years
open('simple/CA.pkey', 'w').write(crypto.dump_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cakey))
open('simple/CA.cert', 'w').write(crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cacert))
for (fname, cname) in [('client', 'Simple Client'), ('server', 'Simple Server')]:
pkey = createKeyPair(TYPE_RSA, 1024)
req = createCertRequest(pkey, CN=cname)
cert = createCertificate(req, (cacert, cakey), 1, (0, 60*60*24*365*5)) # five years
open('simple/%s.pkey' % (fname,), 'w').write(crypto.dump_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, pkey))
open('simple/%s.cert' % (fname,), 'w').write(crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, cert))
|