Preparation 1 sudo apt install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ dpkg -l | grep armel ii cpp-arm-linux-gnueabi 4:9.3.0-1ubuntu2 amd64 GNU C preprocessor (cpp) for the armel architecture ii gcc-9-arm-linux-gnueabi 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04cross2 amd64 GNU C compiler (cross compiler for armel architecture) ii gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi 4:9.3.0-1ubuntu2 amd64 GNU C compiler for the armel architecture ii libasan5-armel-cross 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04cross2 all AddressSanitizer -- a fast memory error detector ii libatomic1-armel-cross 10.2.0-5ubuntu1~20.04cross1 all support library providing __atomic built-in functions ii libc6-armel-cross 2.31-0ubuntu7cross1 all GNU C Library: Shared libraries (for cross-compiling) ii libc6-dev-armel-cross 2.31-0ubuntu7cross1 all GNU C Library: Development Libraries and Header Files (for cross-compiling) ii libgcc-9-dev-armel-cross 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04cross2 all GCC support library (development files) ii libgcc-s1-armel-cross 10.2.0-5ubuntu1~20.04cross1 all GCC support library (armel) ii libgomp1-armel-cross 10.2.0-5ubuntu1~20.04cross1 all GCC OpenMP (GOMP) support library ii libstdc++6-armel-cross 10.2.0-5ubuntu1~20.04cross1 all GNU Standard C++ Library v3 (armel) ii libubsan1-armel-cross 10.2.0-5ubuntu1~20.04cross1 all UBSan -- undefined behaviour sanitizer (runtime) ii linux-libc-dev-armel-cross 5.4.0-21.25cross1 all Linux Kernel Headers for development (for cross-compiling)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ dpkg -l linux-libc-dev-armel-cross Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold | Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend |/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad) ||/ Name Version Architecture Description +++-==========================-=================-============-========================================================== ii linux-libc-dev-armel-cross 5.4.0-21.25cross1 all Linux Kernel Headers for development (for cross-compiling)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ dpkg -L libc6-armel-cross /. /usr /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/ld-2.31.so /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libBrokenLocale-2.31.so ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libutil-2.31.so /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/lib /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf /usr/share /usr/share/doc /usr/share/doc/libc6-armel-cross /usr/share/doc/libc6-armel-cross/README /usr/share/doc/libc6-armel-cross/changelog.Debian.gz /usr/share/doc/libc6-armel-cross/changelog.gz /usr/share/doc/libc6-armel-cross/copyright /usr/share/lintian /usr/share/lintian/overrides /usr/share/lintian/overrides/libc6-armel-cross /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/ld-linux.so.3 ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libthread_db.so.1 /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libutil.so.1 /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/lib/sf /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/ld-2.31.so /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/ld-linux.so.3 /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libBrokenLocale-2.31.so ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libutil-2.31.so /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libutil.so.1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ dpkg -L libc6-dev-armel-cross /. /usr /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/include /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/include/a.out.h ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/include/wordexp.h /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/Mcrt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/Scrt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/crt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/crti.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/crtn.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/gcrt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libBrokenLocale.a ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/librt.a /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libutil.a /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf /usr/share /usr/share/doc /usr/share/doc/libc6-dev-armel-cross /usr/share/doc/libc6-dev-armel-cross/README /usr/share/doc/libc6-dev-armel-cross/changelog.Debian.gz /usr/share/doc/libc6-dev-armel-cross/changelog.gz /usr/share/doc/libc6-dev-armel-cross/copyright /usr/share/lintian /usr/share/lintian/overrides /usr/share/lintian/overrides/libc6-dev-armel-cross /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libBrokenLocale.so /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libanl.so ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/libutil.so /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/Mcrt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/Scrt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/crt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/crti.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/crtn.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/gcrt1.o /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libBrokenLocale.a /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libBrokenLocale.so ... /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libutil.a /usr/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libsf/libutil.so
The GCC low-level runtime library GCC provides a low-level library, libgcc.a or libgcc_s.so on some platforms. GCC generates calls to routines in this library automatically, whether it needs to perform some operation that is too compilcated to emit inline cde for.
Most of the routines in libgcc handle arithmetic operations that the target processor cannot perform directly. This includes integer multiply and divide on some machine, and all floating-point and fixed-point operations on other machines. libgcc also includes routines for exception handling, and a handful of miscellaneous operations.
Some of these routines can be defined in mostly machine-independent C. Others must be hand-written in assembly language for each processor that needs them.
Detail info please refer to here .
libatomic - The GNU Atomic library which is a GCC support runtime library for atomic operations not supported by hardware.
u-boot Building u-boot 1 2 3 4 export ARCH=arm export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi- make vexpress_ca9x4_defconfig make -j2
Enabling debug include/configs/vexpress_ca9x4.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #define DEBUG #ifndef __VEXPRESS_CA9X4_H #define __VEXPRESS_CA9X4_H #define CONFIG_VEXPRES_ORIGINAL_MEMORY_MAP #include "vexpress_common.h" #endif
DEBUG macro controls the debug information in u-boot.
Please undefine it for release version.
Enabling mtd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 CONFIG_MTD=y CONFIG_CMD_MTDPARTS=y CONFIG_MTDIDS_DEFAULT="nor0=flash0-0" CONFIG_MTDPARTS_DEFAULT="mtdparts=flash0-0:8m(kernel),56m(rootfs)" CONFIG_MTD_NOR_FLASH=y CONFIG_FLASH_CFI_DRIVER=y CONFIG_FLASH_CFI_MTD=y
It’s not necessary to enable mtd partition support in u-boot.
We just pass proper arguments to kernel then kernel can startup!
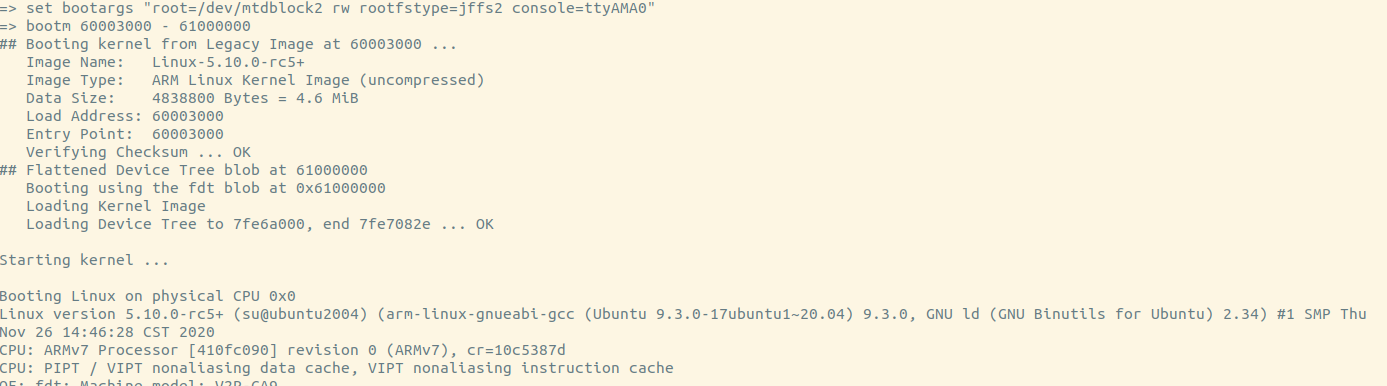
1 set bootargs "console=ttyAMA0 root=/dev/mtdblock2 rootfstype=ext3"
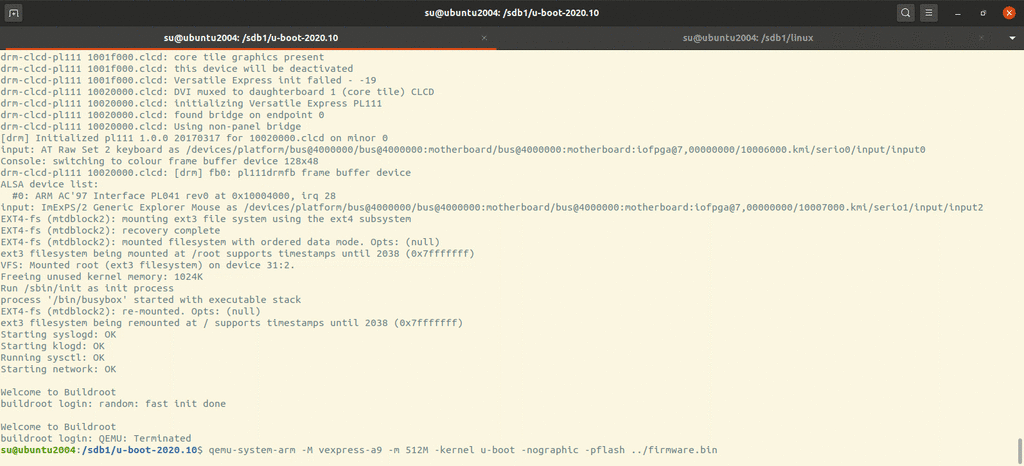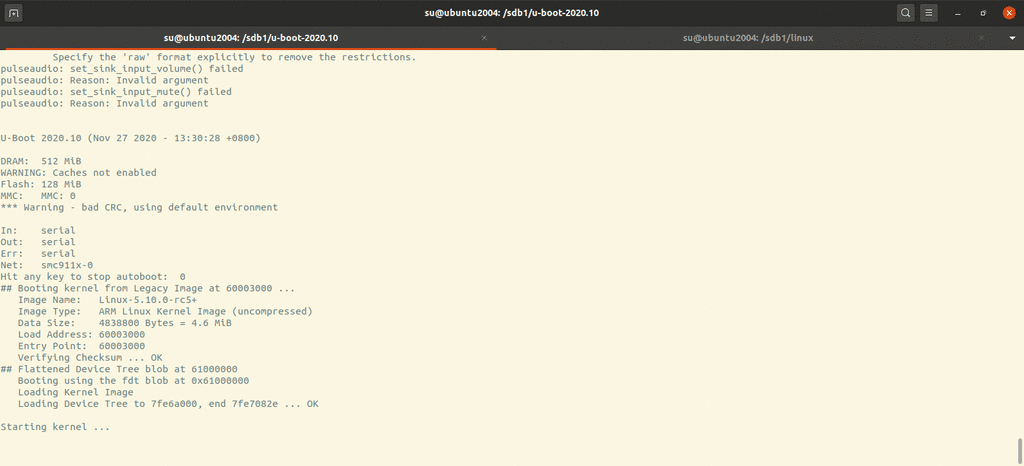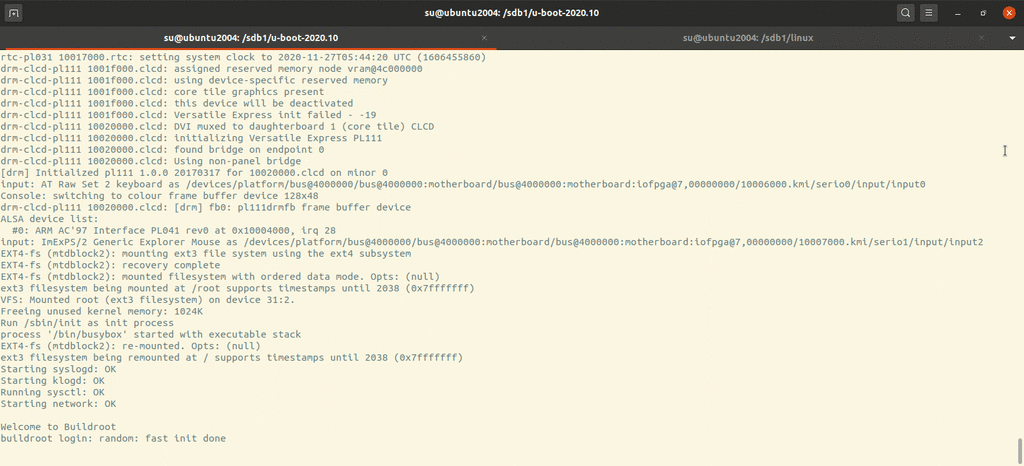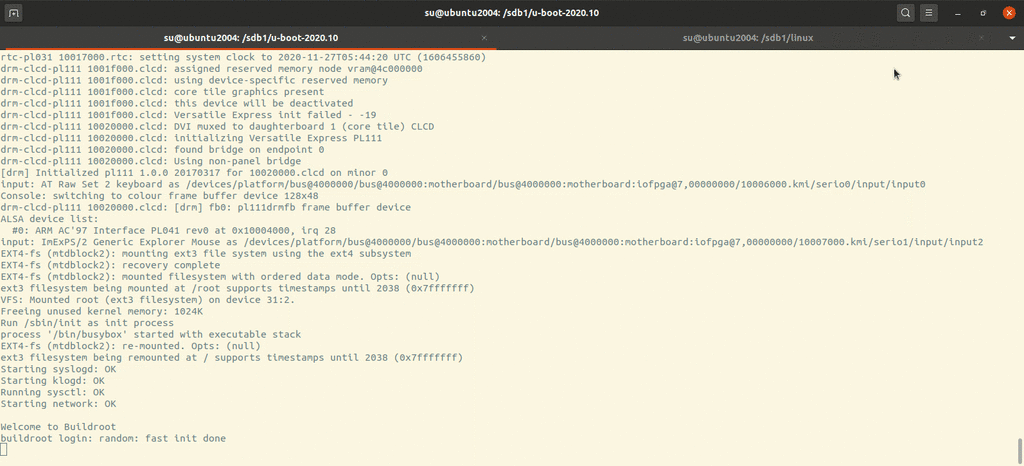
Running u-boot 1 qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -nographic -m 512M -kernel u-boot
Running u-boot with norflash 1 qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -nographic -m 512M -kernel u-boot -pflash firmware.bin
Generating firmware
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 # create 64M image dd if=/dev/zero of=firmware.bin bs=1M count=64 # copy kernel to firmware dd if=uImage of=firmware.bin bs=1M seek=0 conv=notrunc # copy dtb to firmware dd if=vexpress-v2p-ca9.dtb of=firmware.bin bs=1M seek=7 conv=notrunc # copy rootfs to firmware dd if=rootfs.img of=firmware.bin bs=1M seek=8 conv=notrunc
flash image layout
TITLE
range
uImage
0-7M
vexpress-v2p-ca9.dtb
7-8M
rootfs.img
8-64M
rootfs.img is a ext3 file system image.
How to build uImage,dtb,rootfs is in the next part.
Running Example:
u-boot will load kernel from flash then start the kernel.
The kernel will mount rootfs with arguments which are passed from u-boot.
Init will be run and system will startup.
kernel Building kernel 1 2 3 4 5 export ARCH=arm export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi- make O=../vexpress-a9 vexpress_defconfig # generate .config make O=../vexpress-a9 LOADADDR=0x60003000 uImage -j2 # generate uImage make O=../vexpress-a9 dtbs # generate dtbs
Generating partitions As new kernels are all using dts so we need to moidy dts for partitions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 vim arch/arm/boot/dts/vexpress-v2p-ca9.dts &flash0 { partitions { compatible = "fixed-partitions"; #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <1>; kernel: partition@0 { label = "kernel"; reg = <0x00000000 0x00700000>; }; dtb: partition@700000 { label = "dtb"; reg = <0x00700000 0x00100000>; }; rootfs: partition@800000 { label = "rootfs"; reg = <0x00800000 0x03800000>; }; }; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 vim arch/arm/boot/dts/vexpress-v2m.dtsi ... flash0: flash@0,00000000 { compatible = "arm, vexpress-flash", "cfi-flash"; reg = <0 0x00000000 0x04000000>, <1 0x00000000 0x04000000>; bank-width = <4>; partitions { compatible = "arm,arm-firmware-suite"; }; };
flash0 here is alias for flash device in dts file.
We modify it using fixed partition mode, not arm-firmware-suite mode which need each partition must contains self footer information at the end of partition.
Running kernel 1 qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -m 512M -nographic -kernel zImage -dtb vexpress-v2p-ca9.dtb
It will hung up with message:
1 end Kernel panic - not syncing: VFS: Unable to mount root fs on unknown-block(0,0)
As we havent set rootfs!
uclibc-ng As uclibc died, we use uclibc-ng instead.
Refer to document we use command as below.
1 2 cd /sdb1/linux make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi- O=../vexpress_a9 INSTALL_HDR_PATH=../linux-headers
Installation
1 make O=/sdb1/out-uclibc-ng PREFIX=/sdb1/uclibc-ng-install install
After the installation, everything is as below here:
Everything under arm-linux-uclibc/lib/* we need put them in our target rootfs.
usr/* is for building and linking our application which is used by cross-compiler.
On ubuntu 20.04, the arm cross-toolchain using apt is gcc9.3 with glibc 2.31 and kernel header version is 5.4.21 .
So if we want to use uclibc-ng we may need compile gcc ourselves.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 ../uclibc-ng-install/ └── usr └── arm-linux-uclibc ├── lib │ ├── ld-uClibc-1.0.36.so │ ├── ld-uClibc.so.0 -> ld-uClibc.so.1 │ ├── ld-uClibc.so.1 -> ld-uClibc-1.0.36.so │ ├── libc.so.0 -> libuClibc-1.0.36.so │ ├── libc.so.1 -> libuClibc-1.0.36.so │ └── libuClibc-1.0.36.so └── usr ├── include │ ├── alloca.h │ ├── a.out.h ... │ ├── unistd.h │ ├── values.h │ ├── wait.h │ └── wchar.h └── lib ├── crt1.o ├── crti.o ├── crtn.o ├── libc.alibc-2.31.so ├── libc_pic.a -> libc.a ├── libcrypt.a ├── libcrypt_pic.a -> libcrypt.a ├── libc.so ├── libdl.a ├── libdl_pic.a -> libdl.a ├── libnsl.a ├── libnsl_pic.a -> libnsl.a ├── libpthread_nonshared.a ├── libpthread_nonshared_pic.a -> libpthread_nonshared.a ├── libresolv.a ├── libresolv_pic.a -> libresolv.a ├── librt.a ├── librt_pic.a -> librt.a ├── Scrt1.o └── uclibc_nonshared.a
usr/include/* and usr/lib/* are for compiler to link with.
lib/* are the runtime shared libraries for applications.
rootfs Building busybox with static link 1 2 3 4 5 6 export ARCH=arm export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi- make defconfig make menuconfig # setting build option with Build static binary (no shared libs) make -j2 make install # will create _install directory with all thins in it
Or default building mode is shared, so we need copy all shared libraries to system rootfs.
cp /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/.so. rootfs/lib -arf
If we want to use arm-linux-gnueabi toolchain, the size of libraries is aboud 16M. Maybe we should build our uclibc toolchain .
Making rootfs ext3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 # !/bin/bash base=`pwd` tmpfs=/_tmpfs sudo rm -rf rootfs sudo rm -rf ${tmpfs} sudo rm -f a9rootfs.ext3 sudo mkdir rootfs sudo cp _install/* rootfs/ -raf cd rootfs && sudo mkdir -p lib proc sys tmp root var mnt && cd ${base} # add shared runtime libraries from arm-linux-gnueabi (glibc 2.31) sudo cp /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/*.so.* rootfs/lib -arf sudo cp examples/bootfloppy/etc rootfs/ -arf sudo sed -r "/askfirst/ s/.*/::respawn:-\/bin\/sh/" rootfs/etc/inittab -i sudo mkdir -p rootfs/dev/ sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty1 c 4 1 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty2 c 4 2 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty3 c 4 3 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty4 c 4 4 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/console c 5 1 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/null c 1 3 sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=a9rootfs.ext3 bs=1M count=64 sudo mkfs.ext3 a9rootfs.ext3 sudo mkdir -p ${tmpfs} sudo chmod 777 ${tmpfs} sudo mount -t ext3 a9rootfs.ext3 ${tmpfs}/ -o loop sudo cp -r rootfs/* ${tmpfs}/ sudo umount ${tmpfs}
jffs2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 # !/bin/bash base=`pwd` sudo rm -rf rootfs sudo rm -f a9rootfs.jffs2 sudo mkdir rootfs sudo cp _install/* rootfs/ -raf cd rootfs && sudo mkdir -p lib proc sys tmp root var mnt && cd ${base} # add shared runtime libraries from arm-linux-gnueabi (glibc 2.31) sudo cp /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi/lib/*.so.* rootfs/lib -arf sudo cp examples/bootfloppy/etc rootfs/ -arf sudo sed -r "/askfirst/ s/.*/::respawn:-\/bin\/sh/" rootfs/etc/inittab -i sudo mkdir -p rootfs/dev/ sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty1 c 4 1 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty2 c 4 2 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty3 c 4 3 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty4 c 4 4 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/console c 5 1 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/null c 1 3 # 56M, no cleanmarker sudo mkfs.jffs2 -r ./rootfs -o a9rootfs.jffs2 -pad 0x3800000 -n
initrd initramfs vs initrd
The first question : Are they the same thing?
Note from here :
If an initramfs is built into kernel or passed to it, the kernel will try to execute /init in the initramfs. Usually /init is as shell script that will find and mount the root partition, then switch_root onto the root partition and execute /sbin/init.
The initramfs can be built into kernel with CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE which is the rootfs directory in local file system.
The standalone initramfs is also ok in which case we need tell the bootloader where initramfs is.
Generating initrd
1 find . | cpio --quiet -H newc -o | gzip -9 -n > myinitrd
Running kernel with standalone initrd
qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -m 512M -kernel zImage -initrd initrd.img -dtb vexpress-v2p-ca9.dtb -nographic -append “console=ttyAMA0 rdinit=/linuxrc”
If the initramfs doesnot have /init then kernel panic with message:
Kernel panic - not syncing: VFS: Unable to mount root fs on unknown-block(1,0)
If we really dont want to have such “/init” , we can append the kernel args to workaround it.
rdinit=/linuxrc
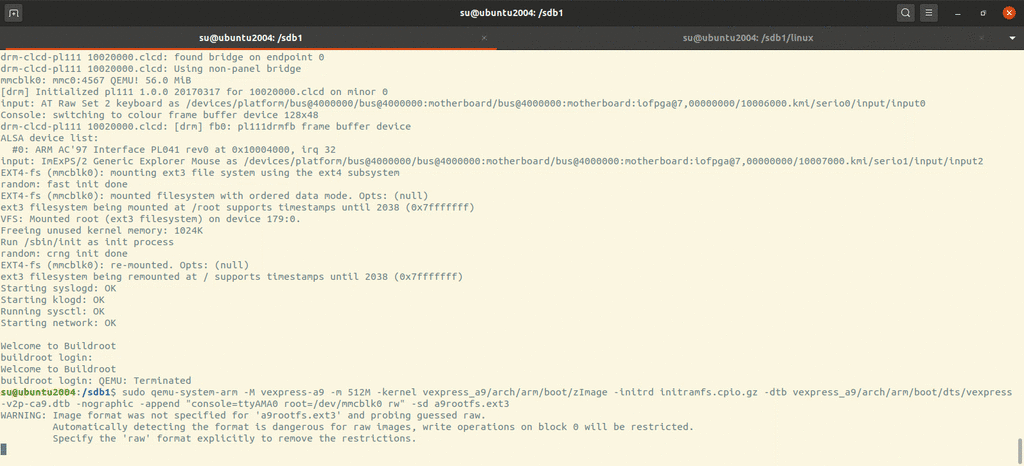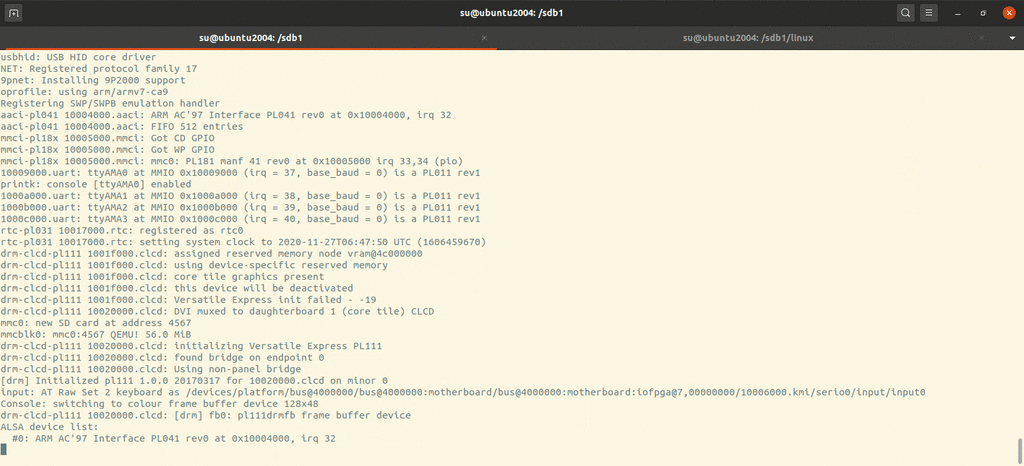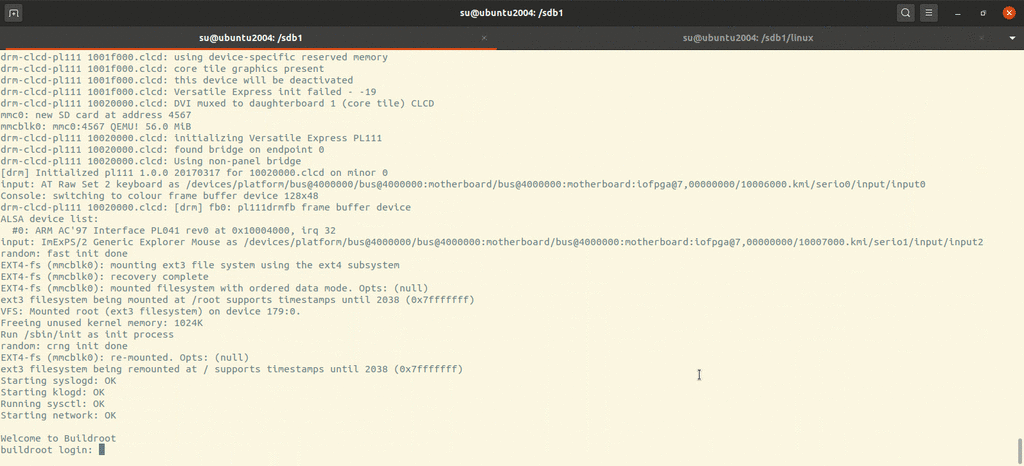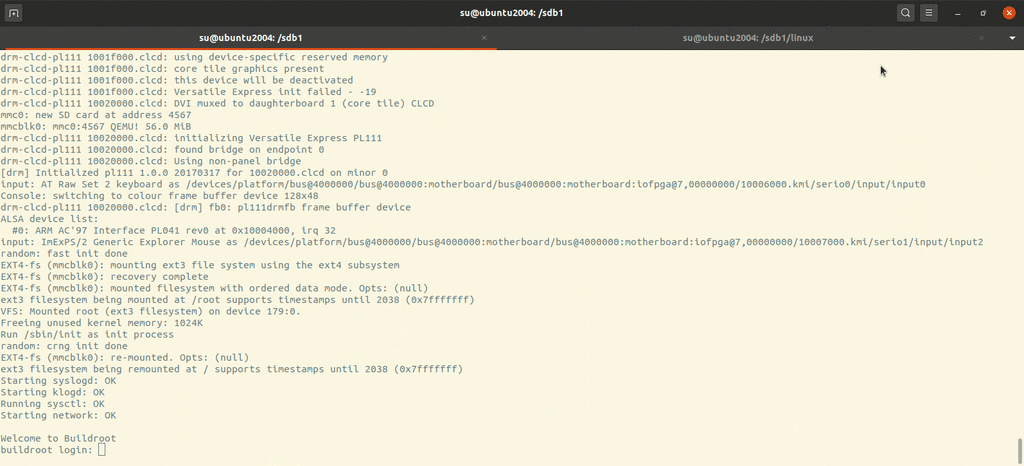
Running kernel with rootfs 1 qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -m 512M -nographic -kernel zImage -dtb vexpress-v2p-ca9.dtb -append "root=/dev/mmcblk0 rw console=ttyAMA0" -sd a9rootfs.ext3
Here we use the partition at sd card as the rootfs.
static or shared for library We can use installed arm-linux-gnueabi toolchain to build shared or static applications. For “shared” building we need runtime shared libraries(glibc and gcc runtime libraries such as libgcc libatomic) to rootfs.
If we want to use uclibc we need more hacks so we build ourselves toolchain using buildroot .
buildroot Downloading https://buildroot.org/downloads/buildroot-2020.02.8.tar.gz
Configuration and building
we can set linux kernel headers which the toolchain may use and which lib we use (glibc, uclibc, musl).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ tree -L 1 . ├── arch ├── board ├── boot ├── CHANGES ├── Config.in ├── Config.in.legacy ├── configs ├── COPYING ├── DEVELOPERS ├── dl ├── docs ├── fs ├── linux ├── Makefile ├── Makefile.legacy ├── output ├── package ├── README ├── support ├── system ├── toolchain └── utils
output/ has all things we need.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ tree output -L 1 output ├── build ├── host ├── images ├── staging -> /sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8/output/host/arm-buildroot-linux-uclibcgnueabi/sysroot └── target 5 directories, 0 files
host/ is our cross compile toolchain.
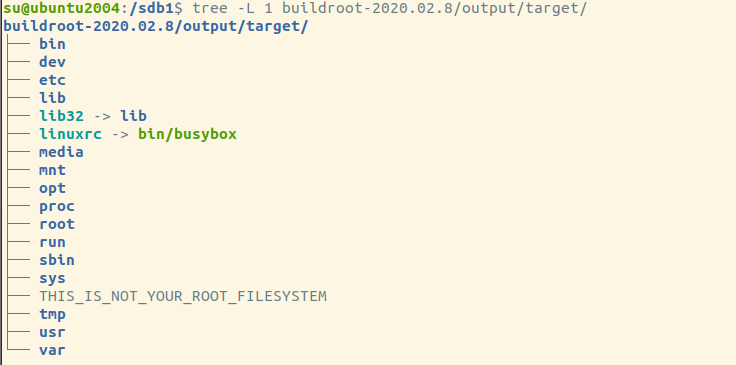
target/ has our rootfs directory which busybox and gcc/uclibc runtime shared libraries are all there.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8$ tree output/host/arm-buildroot-linux-uclibcgnueabi/sysroot/ -L 2 output/host/arm-buildroot-linux-uclibcgnueabi/sysroot/ ├── bin ├── dev │ ├── fd -> ../proc/self/fd │ ├── stderr -> ../proc/self/fd/2 │ ├── stdin -> ../proc/self/fd/0 │ └── stdout -> ../proc/self/fd/1 ├── etc │ ├── group │ ├── hosts │ ├── mtab -> ../proc/self/mounts │ ├── passwd │ ├── profile │ ├── profile.d │ ├── protocols │ ├── resolv.conf -> ../tmp/resolv.conf │ ├── services │ └── shadow ├── lib │ ├── ld-uClibc-1.0.32.so │ ├── ld-uClibc.so.0 -> ld-uClibc.so.1 │ ├── ld-uClibc.so.1 -> ld-uClibc-1.0.32.so │ ├── libatomic.a │ ├── libatomic.la │ ├── libatomic.so -> libatomic.so.1.2.0 │ ├── libatomic.so.1 -> libatomic.so.1.2.0 │ ├── libatomic.so.1.2.0 │ ├── libc.so.0 -> libuClibc-1.0.32.so │ ├── libc.so.1 -> libuClibc-1.0.32.so │ ├── libgcc_s.so │ ├── libgcc_s.so.1 │ └── libuClibc-1.0.32.so ├── lib32 -> lib ├── media ├── mnt ├── opt ├── proc ├── root ├── run ├── sbin ├── sys ├── tmp └── usr ├── bin ├── include ├── lib ├── lib32 -> lib ├── sbin └── share 22 directories, 26 files
1 /sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8/output/host/bin/arm-buildroot-linux-uclibcgnueabi-gcc hello.c -o hello
1 2 su@ubuntu2004:/sdb1/hello-world$ file hello hello: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, EABI5 version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-uClibc.so.0, not stripped
Building a application using our self-building toolchain.
Generating our custom rootfs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 # !/bin/bash base=`pwd` tmpfs=/_tmpfs sudo rm -rf rootfs sudo rm -rf ${tmpfs} sudo rm -f a9rootfs.ext3 sudo mkdir rootfs sudo cp /sdb1/buildroot-2020.02.8/output/target/* rootfs/ -raf sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty1 c 4 1 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty2 c 4 2 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty3 c 4 3 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/tty4 c 4 4 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/console c 5 1 sudo mknod rootfs/dev/null c 1 3 sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=a9rootfs.ext3 bs=1M count=64 sudo mkfs.ext3 a9rootfs.ext3 sudo mkdir -p ${tmpfs} sudo chmod 777 ${tmpfs} sudo mount -t ext3 a9rootfs.ext3 ${tmpfs}/ -o loop sudo cp -r rootfs/* ${tmpfs}/ sudo umount ${tmpfs}
We should create all the needed device files by ourselves!
Running the kernel and rootfs 1 sudo qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -m 512M -kernel vexpress_a9/arch/arm/boot/zImage -dtb vexpress_a9/arch/arm/boot/dts/vexpress-v2p-ca9.dtb -nographic -append "root=/dev/mmcblk0 rw console=ttyAMA0" -sd a9rootfs.ext3
Running example:
Making firmware Now we’ve building u-boot, kernel, dtb, rootfs. It’s time for us to custom our firmware.
Defining default u-boot arguments
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #define CONFIG_EXTR_ENV_SETTINGS \ CONFIG_PLATFORM_ENV_SETTINGS \ BOOTENV \ "console=ttyAMA0,38400n8\0" \ "root=/dev/mtdblock2\0" \ "rootfstype=jffs2\0" \ "flashargs=setenv bootargs root=${root} rw rootfstype=${rootfstype} console=${console}\0" \ "bootflash=run flashargs; " \ "cp 40000000 60003000 500000; " \ "cp 40700000 61000000 100000; " \ "bootm 60003000 - 61000000\0" \ "fdtfile=" CONFIG_DEFAULT_FDT_FILE "\0"
Generating firmware
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # !/bin/bash # create nor flash image dd if=/dev/zero if=firmware.bin bs=1M count=64 # kernel 0-7M dd if=vexpress-a9/arch/arm/boot/uImage of=firmware.bin bs=1M seek=0 conv=notrunc # kernel 7-8M dd if=vexpress-a9/arch/arm/boot/dts/vexpress-v2p-ca.dtb of=firmware.bin bs=1M seek=7 conv=notrunc # rootfs 8-64M dd if=a9rootfs.jffs2 of=firmware.bin bs=1M seek=8 conv=notrunc sync echo "firmware is ok!"
Running firmware
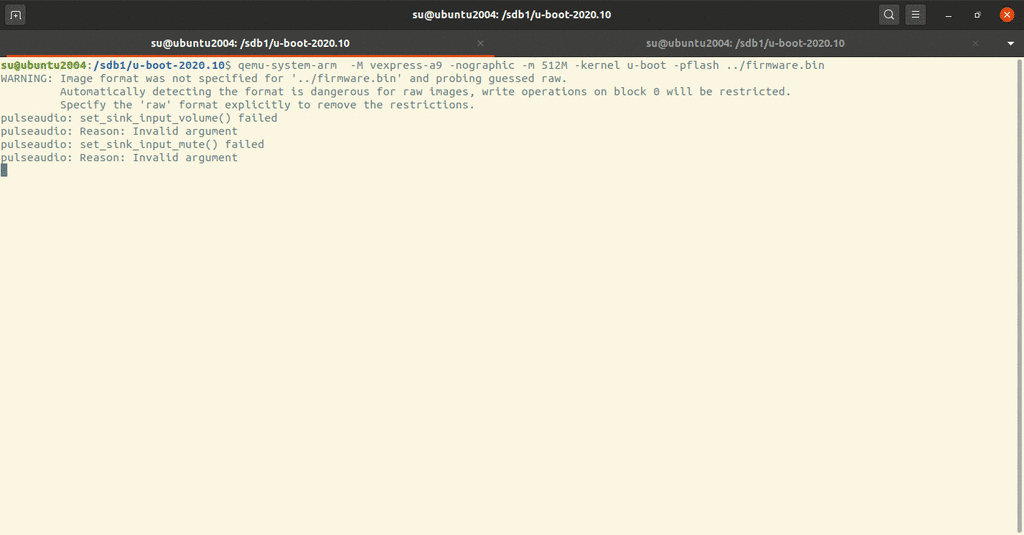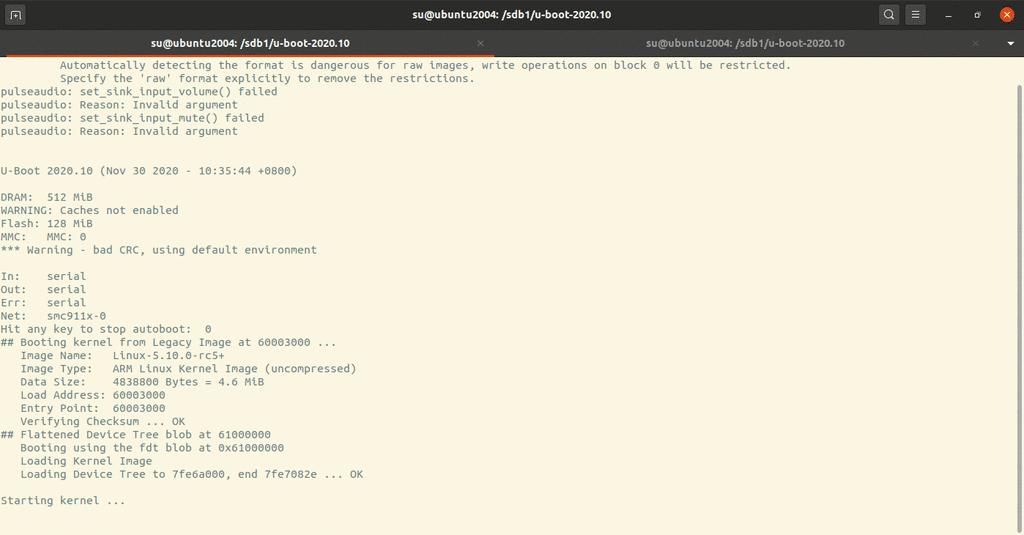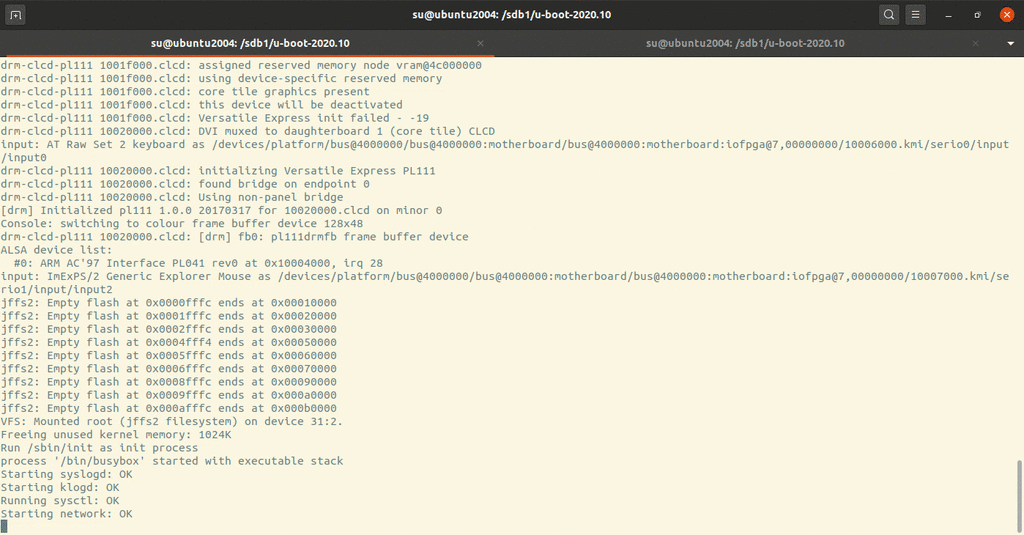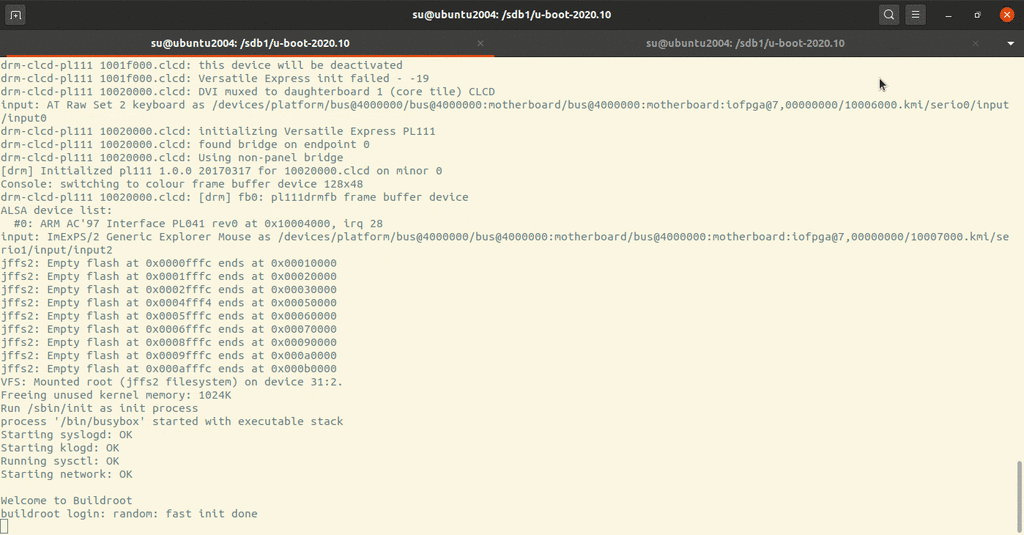
1 qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -nographic -m 512M -kernel u-boot -pflash ../firmware.bin
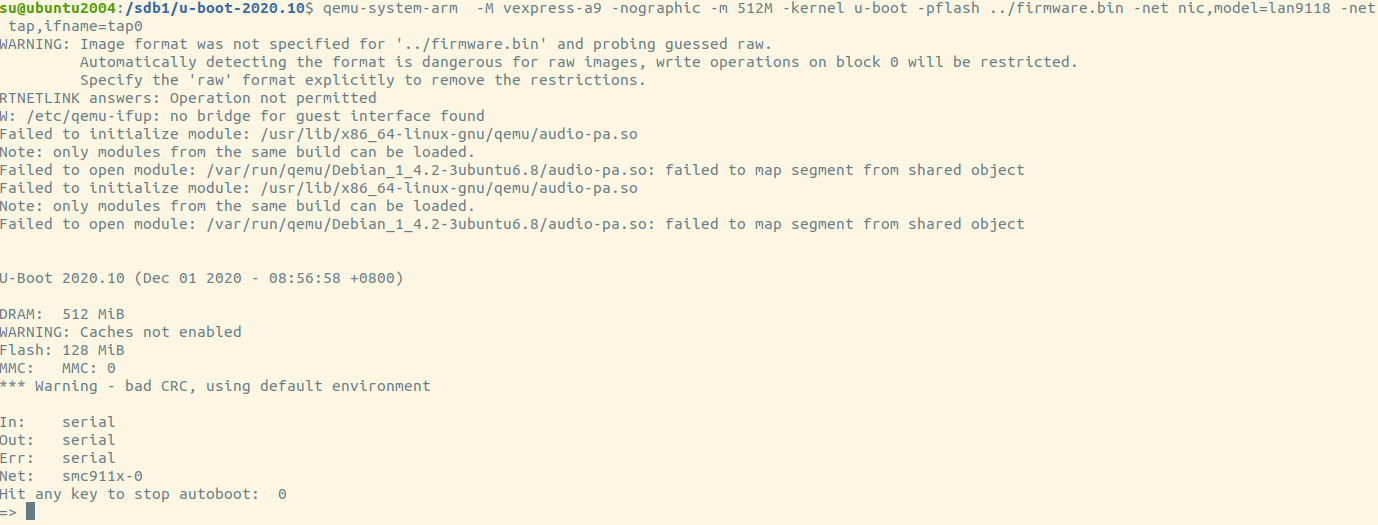
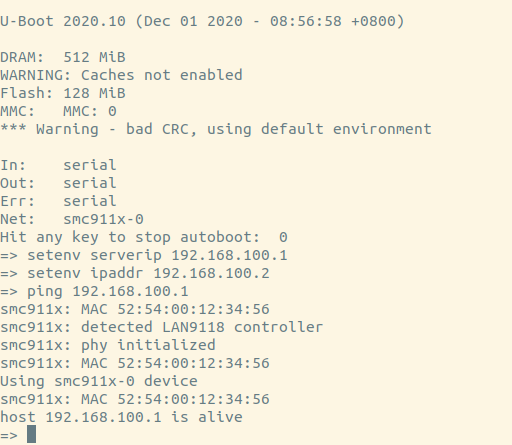
Using tftp 1 qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -nographic -m 512M -kernel u-boot -pflash ../firmware.bin -net nic,model=lan9118 -net tap,ifname=tap0
“-net nic,model=lan9118 -net tap,ifname=tap0” for qemu. It’ll use tap0 as it’s simulated nic.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 # create tap0 sudo tunctl -u $(whoami) -t tap0 # create br0 sudo brctl addbr br0 # add tap0 to br0 sudo brctl addif br0 tap0 # bring up br0 sudo ifconfig br0 up # bring up tap0 sudo ifconfig tap0 up # setting ip of br0 sudo ifconfig br0 192.168.100.1/24
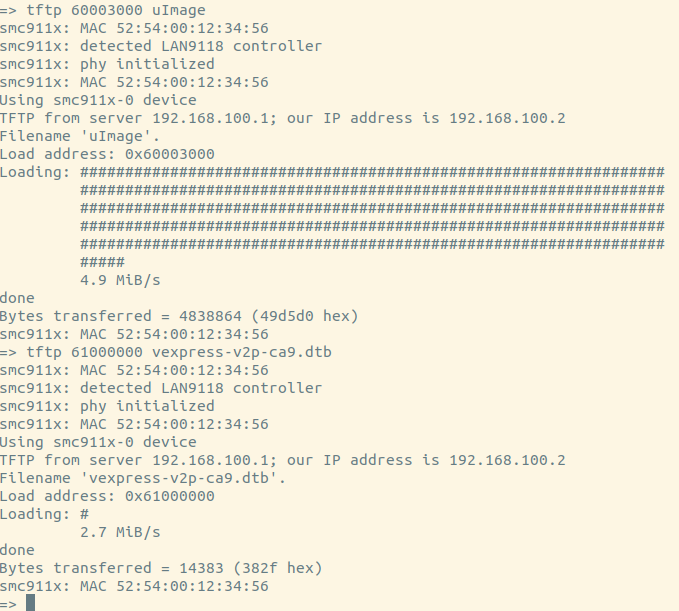
So we can update kernel or rootfs by network now!
References
understanding-how-bootloader-works-by-creating-your-own-firmware arm-emulated-environment-iotsec-qemu howto-initramfs-image How can I print more debug information from U-boot Build and run minimal Linux / Busybox systems in Qemu Using the initial RAM disk arm-emulated-environment-iotsec-qemu Passing Kernel Arguments how to adress flash memory in Linux